Using DeepLabCut#
This guide, and related pages, are meant as a very-new-to-python beginner guide to DeepLabCut. After you are comfortable with this material we recommend then jumping into the more detailed User Guides!
ProTip: For even more ‘in-depth’ understanding, head over to check out the DeepLabCut Course, which provides a deeper dive into the science behind DeepLabCut.
Installation#
Before you begin, make sure that DeepLabCut is installed on your system.
ProTip: For detailed installation instructions, geared towards a bit more advanced users, refer to the Full Installation Guide.
Beginner User Guide#
If you are new to Python, the best way to get Python installed onto your computer is with Anaconda. Head over here and download the version that is best for your computer.
“Conda”, as it’s often called, it a very nice way to create “environments (env)” on your computer. While there can be some cross-talk, in general, it allows you to separate the different tools you need to use to get your science done 💪.
Let’s learn a bit and create a DeeplabCut env:#
After you have installed Anaconda, open the new program (Anaconda Terminal). You will be in your “root” directory by default.
(0) Create a fresh conda environment
In the terminal, type:
conda create -n deeplabcut python=3.10
You will be prompted (y/n) to install, and then wait for the magic to happen. At the end, check the terminal, it should prompt you to then type:
conda activate deeplabcut
Now, we are going to install the core dependencies. The way this works is that there are “package managers” such as conda itself and python’s pip. We are going to deploy a mix based on what we know works across ooperating systems.
(1) Install PyTorch
PyTorch is the backend deep-learning language we wrote DLC3 in. To select the right version, head to the “Install PyTorch” instructions in the official PyTorch Docs. Select your desired PyTorch build, operating system, select conda as your package manager and Python as the language. Select your compute platform (either a CUDA version or CPU only). Then, use the command to install the PyTorch package. Below are a few possible examples:
GPU version of pytorch for CUDA 12.4
pip install torch torchvision --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu124
CPU only version of pytorch, using the latest version
pip install torch torchvision --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cpu
(2) Install DeepLabCut
Alright! Next, we will install all the deeplabcut source code 🔥. Please decide which version you want (stable or alpha), then type:
For the Stable release:
pip install "deeplabcut[gui,modelzoo,wandb]"
This gives you DeepLabCut, the DLC GUI (gui), our latest neural networks (modelzoo) and a cool data logger (wandb) if you choose to use it later on!
OR for the Alpha release (from GitHub bleeding edge of the code):
pip install "git+https://github.com/DeepLabCut/DeepLabCut.git@pytorch_dlc#egg=deeplabcut[gui,modelzoo,wandb]"
Starting DeepLabCut#
In the terminal, enter:
python -m deeplabcut
This will open the DeepLabCut App (note, the default is dark mode, but you can click “appearance” to change:
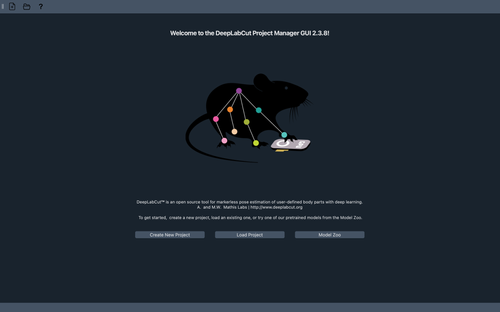
💡 Note: For a visual guide on navigating through the DeepLabCut GUI, check out our YouTube tutorial.
Starting a New Project#
Commencing Your Work:#
For a first-time or new user, please click on
Start New Project.
🐾 Steps to Start a New Project#
Launch New Project:
When you start a new project, you’ll be presented with an empty project window. In DLC3+ you will see a new option “Engine”.
We recommend using the PyTorch Engine:
 )
)
Filling in Project Details:
Naming Your Project:
Give a specific, well-defined name to your project.
💡 Tip: Avoid empty spaces in your project name.
Naming the Experimenter:
Fill in the name of the experimenter. This part of the data remains immutable.
Determine Project Location:
By default, your project will be located on the Desktop.
To pick a different home, modify the path as needed.
Multi-Animal or Single-Animal Project:
Tick the ‘Multi-Animal’ option in the menu, but only if that’s the mode of the project.
Choose the ‘Number of Cameras’ as per your experiment.
Adding Videos:
First, click on
Browse Videosbutton on the right side of the window, to search for the video contents.Once the media selection tool opens, navigate and select the folder with your videos.
💡 Tip: DeepLabCut supports
.mp4,.avi,.mkvand.movfiles.A list will be created with all the videos inside this folder.
Unselect the videos you wish to remove from the project.
Create your project:
Click on
Createbutton on the bottom, right side of the main window.A new folder named after your project’s name will be created in the location you chose above.
📽 Video Tutorial: Setting Up Your Project in DeepLabCut#